Reiki is a spiritual practice developed in 1922 by Japanese Buddhist Mikao Usui, which has since been adapted by various teachers of varying traditions.
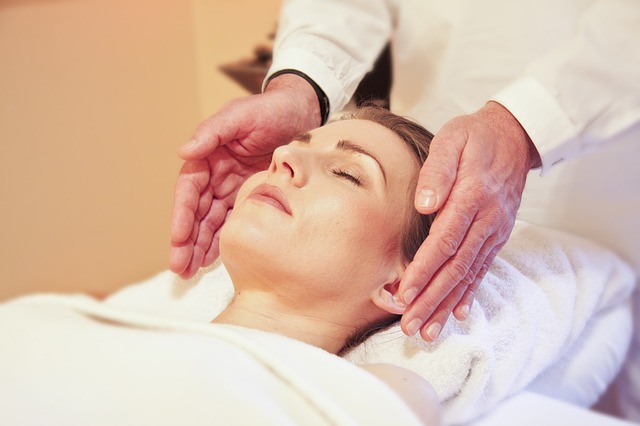
It uses a technique commonly called palm healing or hands on healing as a form of alternative medicine and is sometimes classified as oriental medicine by some professional medical bodies.
Through the use of this technique, practitioners are transferring universal energy (i.e., reiki) in the form of qi (Japanese: ki) through the palms, which allows for self-healing and a state of equilibrium.
There are two main branches of Reiki, commonly referred to as Traditional Japanese Reiki and Western Reiki.
Though differences can be wide and varied between both branches and traditions, the primary difference is that Westernised forms use systematised hand-placements rather than relying on an intuitive sense of hand-positions, which is commonly used by Japanese Reiki branches.
Both branches commonly have a three-tiered hierarchy of degrees, usually referred to as the First, Second, and Master/Teacher level, all of which are associated with different skills and techniques. There are over 140 different disciplines of Reiki.
The English word reiki derives from the Japanese loanword reiki (meaning “mysterious atmosphere”), which derives from the Chinese loanword língqì (“supernatural influence”).
Its earliest recorded usage in English dates to 1975. Instead of the usual transliteration, some English-language authors pseudo-translate reiki as “universal life energy”.
Courtesy of Wikipedia