While taking a shower or brushing your hair, you notice more hair in the drain or on your brush than usual. This can be pretty frightening. We are going to go over some pretty common reasons as to why your hair may be falling out.
So stomp that pang of fear down and read on.
Hereditary
Hereditary hair loss is hair loss that has to do with genetics. This is also the most common reason for hair loss. It will usually begin with a thinning hairline above your forehead.
It develops slowly and can begin in women as early as their 20’s. You can try slowing down this type of hair loss by applying Rogaine to the baring spots up to twice daily.
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Iron deficiency anemia can cause you to lose your hair as well. When we have an iron deficiency our blood doesn’t carry red blood cells throughout the body like it is supposed to This can also cause a lack of oxygen in our cells.
When cells don’t have oxygen they fail to reproduce. Hence, no hair reproduction in the spots where your hair is falling out. If you want to combat this type of hair loss, try eating foods rich in iron and protein and take a multivitamin with iron once daily.
Skin Conditions Of The Scalp
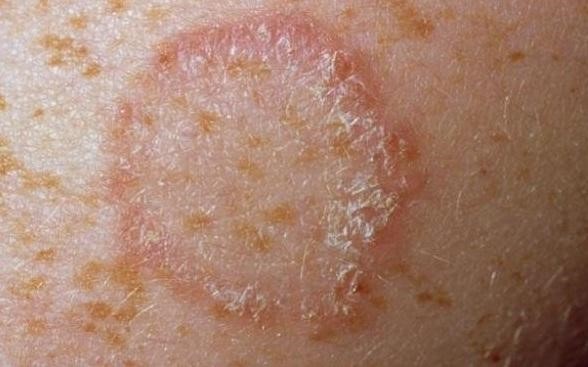
Having an unhealthy scalp can make it hard for your hair to grow. Some conditions of the skin that can cause hair loss are: dandruff, psoriasis, and certain fungal infections such as ringworm.
To fight these maladies make an appointment with your dermatologist and purchase the best hair brush for your hair type or hair styles. They will likely write you out a prescription for some creams that you can apply to these areas.
Once these problem areas are under control you should start to see hair growth and regeneration.
Excessive Heat Styling
Excessive styling can not only make your hair fall out but it can cause severe damage to the hair that you do have. Heat styling strips your hair of its natural oils forcing it to become dry, brittle, and broken.
Try to let your hair air dry when possible and using the best hair brush for your hair type gently brush it when wet, cut back on styling products, and try sleeping in curlers instead of heat curling your hair.
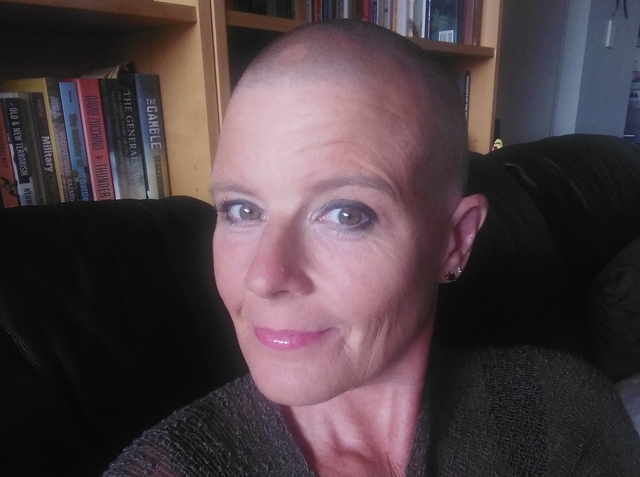
Alopecia
Alopecia is a condition in which the immune system attacks otherwise healthy hair follicles. It is not truly known what causes this distressing disorder, though it is though stress or illness may trigger it.
It occurs equally in men and women. In some cases Rogaine can help with hair regeneration. In other cases corticosteroids may be prescribed to help.
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Polycystic ovarian syndrome affects nearly 5 million women in the united states alone. It is caused when the ovaries produce extremely too much male hormone.
It can begin in females as early as the age of 11 and is characterized by excessive facial hair or hair loss on the scalp. This condition can usually be brought under control by taking birth control prescribed by a doctor.
Lupus
Lupus is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the body’s healthy tissues. A common symptom of lupus is mild to moderate hair loss as well as the characteristic butterfly rash across the cheeks and the bridge of the nose.
Common treatments include oral prednisone if joints and inflammation are involved and a topical cream if there is a rash on the scalp.
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is a disease of the thyroid gland. This disease causes your thyroid to produce too little of the thyroid hormone. It is also known as an underactive thyroid.
The growth of your hair, skin, and nails all depend on this hormone so all functions slow down critically when the thyroid doesn’t produce it. This is easily fixed though, with a thyroid hormone regulating medication that your doctor can prescribe.
This is not a complete list of the reasons you may be losing your hair, these are just the most common. The only way to know the underlying reasons for sure is to visit your doctor. As you can tell, most issues are easily fixed.
NOTE: Many of these disorders are autoimmune disorders. You can learn so much more about this in this free magazine on the autoimmune system.
You can find much more information on living a holistic lifestyle in these free magazines and on our YouTube channel.
 Bio:
Bio: